Manufacturing Engineering (MFE)
The BS degree program in Manufacturing Engineering is dedicated to undergraduate manufacturing engineering education and is accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (EAC/ABET), http://www.abet.org.

Manufacturing Engineering Trends
Manufacturing is one of the major wealth-producing sectors of the world economic structure with a direct and powerful impact on the quality of life of everyone. The field of manufacturing has undergone dramatic changes during the past decade. Diverse forces driving these changes include the following factors: rapid technological advances in areas such as computers, lasers, machine vision, robotics and automation; emerging new materials including polymers, composites and ceramics; an increasing global economy with intensified international trade competition; changing national defense and security priorities; changing labor management relationships; dwindling natural resources; increasing energy costs; bio-socio-educational factors impacting educational access and delivery and heightened environmental concerns.
These factors continue to produce new demands and exciting opportunities for manufacturing engineers. Graduates of the program have found diverse employment in manufacturing fields such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, defense, food processing, and consumer product industries. Graduates of the Manufacturing Engineering program are in great demand from prestigious firms and government agencies. Others have earned related graduate degrees at some of the nation’s finest graduate engineering schools prior to assuming industry positions.
MFE Program Educational Objectives (PEOs)
The Manufacturing Engineering program at Central State University is dedicated to preparing students for manufacturing engineering careers in diverse manufacturing enterprises. The MFE Program expects the graduates within a few years of graduation to attain the following objectives:
- Have productive careers.
- Embrace leadership opportunities, promote diversity, and communicate effectively.
- Pursue professional development and continuing education.
- Adhere to the Engineer’s code of conduct and ethics.
- Positively contribute to the university, local communities, and global societies.
The Bachelor of Science degree program in Manufacturing Engineering has been designed to address these objectives. The curriculum follows guidelines established by the Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME), an international organization headquartered in Southfield, Michigan, with over 30,000 members in seventy-two (72) countries. SME seeks
to ensure that Manufacturing Engineering programs produce engineers prepared to address industry demands for increasingly sophisticated manufacturing technology, and ready to play an important role in planning, building, and optimizing the “factories of the future.” Emphasis is, therefore, given to computer-aided design and manufacturing
(CAD/CAM), layered manufacturing or 3-D printing, microprocessor control, manufacturing planning and control, quality and reliability assurance, metrology and the processing and utilization of engineering materials. The program provides opportunities for hands-on experience in the application of the knowledge embodied in these disciplines. The BS degree program in Manufacturing Engineering is one of only a few programs in the nation which are dedicated to undergraduate manufacturing engineering education, and which are accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (EAC/ABET), http://www.abet.org .
The overarching goal of the program is to produce graduates who are well prepared to:
- Contribute to the engineering planning and management of a relatively large, modern manufacturing operation.
- Introduce modern manufacturing methods and design technologies into a small manufacturing operation or assist in the start-up of a new manufacturing enterprise.
- Maintain a process of life-long learning to retain technical competence, including earning graduate degrees in engineering or related business management or other professional studies and obtaining relevant professional certification.
The overall Manufacturing Engineering curriculum consists of strong components of mathematics, basic sciences, engineering sciences, humanities, and social sciences, together with the major engineering requirements, which can be grouped into the following topic areas:
Materials and Manufacturing Processes — the structure and property relationships of materials and their change with materials processing.
Process, Assembly, and Product Engineering — the design of products and the equipment, tooling, and environment necessary for their manufacture, supported by rapid prototyping and 3-D layered manufacturing.
Manufacturing Competitiveness — the creation of competitive advantage through manufacturing planning, strategy, and control. Topics such as productivity, quality, reliability, economic and cost analysis, human resources, product safety and liability, social concerns, international issues, environmental impact, and product life cycle are included in this area.
Manufacturing Systems Design — the analysis, synthesis, and control of manufacturing operations emphasizing modern technologies and tooling and statistical and calculus-based methods.
Simulation and Information Technology — Simulation, modeling, control, architecture, and information systems supported by experimental design for factory optimality control are included in this area.
Laboratory Experience - Measuring manufacturing process variables in a manufacturing laboratory and making technical inferences about the process. Throughout the curriculum major emphasis is given to the engineering design function.
The Engineering Accreditation Commission of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (EAC/ABET) has published the following description for engineering design:
Engineering design is the process of devising a system, component, or process to meet desired needs. It is a decision-making process (often iterative), in which the basic sciences, mathematics, and engineering sciences are applied to convert resources optimally to meet a stated objective. Among the fundamental elements of the design process are the establishment of objectives and criteria, synthesis, analysis, construction, testing and evaluation. The engineering design component of a curriculum must include most of the following features: development of student creativity, use of open-ended problems, development and use of modern design theory and methodology, formulation of design problem statements and specifications, consideration of alternative solutions, feasibility considerations, production processes, concurrent engineering design, and detailed system descriptions. Further, it is essential to include a variety of realistic constraints, such as economic factors, safety, reliability, aesthetics, ethics and social impact.
In the senior year, the design experience culminated with a sequenced two-semester “capstone” design project. Students work on individual or team design projects under close faculty supervision. A broad range of resources, including machine tools, materials testing and processing equipment, electronic and measuring instrumentation, computers, and control devices, is available to prepare students for the real-world challenges of the engineering profession. Oral and written communication skills are emphasized in the senior design project.
Student Outcomes (SOs) for MFE Curriculum
The broad educational experience outlined above is designed to integrate the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values acquired in a diverse set of courses to produce graduates with the following specific student outcomes:
- an ability to identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems by applying principles of engineering, science, and mathematics
- an ability to apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs with consideration of public health, safety, and welfare, as well as global, cultural, social, environmental, and economic factors
- an ability to communicate effectively with a range of audiences
- an ability to recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations and make informed judgments, which must consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts
- an ability to function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks, and meet objectives
- an ability to develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret data, and use engineering judgment to draw conclusions
- an ability to acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies.
Program map
-
First time students
- Complete Math | English | Biology | Chemistry requirements
- Complete Introductory Major MFE courses
- Complete Remedial Math & Science Courses (if needed)
- Complete First Year Seminar Course
- Academic Advising (Heavy) | Faculty Advising (Introduction)
- Explore Research Apprenticeships | Internships
- Involve Professional Societies | Honor Societies
-
Undeclared to STEM
Transfer Students
- Complete Engineering Science Courses
- Complete Advanced Math & Biology courses
- Complete other General Education courses
- Faculty Advising
- Explore undergraduate research/internships
- Involve Professional Societies | Honor Societies (lower-level leadership)
-
2+2 Transfer Students
- Complete Manufacturing Engineering Theory courses
- Complete Initial level design courses
- Take Minor courses
- Faculty Advising
- Enhance undergraduate research/internships
- Research presentations & Attend conferences
- Involve Professional Societies | Honor Societies (middle level leadership)
- Engage Peer Mentoring & Tutoring
- Attend Career Fairs & Networking
-
- Complete Advanced Manufacturing Engineering Courses
- Complete Capstone design project
- Complete optional Certificate & Minor courses
- Faculty Advising | Career Service Advising
- Take GRE and Apply for Graduate and Professional Programs
- EIT licensure and certification exams
- Research presentations, Attend conferences, Publish papers
- Involve Professional Societies | Honor Societies (Upper-level leadership)
- Engage Peer Mentoring & Tutoring
- Attend Career Fairs, Networking, Resume Writing & Job Interviews
Graduate to Industry
Graduate Schools
-
Year 4+
- Degree Awarded
- Post graduate surveys
- Get Official Transcripts
- Beg your post-CSU Experience
- Complete advanced coursework
- Attend Graduate and Professional Schools
- Pass licensure exams
- Enter workforce
DEGREE REQUIREMENTS A total of 123 semester hours are required for the BS degree in manufacturing engineering:
GENERAL EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS (Min 39-40 hours): Twenty-seven of a total fifty (50) credits apply also to the manufacturing engineering (MFE) program requirements; see University General Education Requirements.
MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS:
The majority of the MFE courses emphasize design, the process of devising a system, component, or process to meet some desired need. The design course work provides experience in open-ended problem solving by combining decision 186 making and creative thought with basic and engineering sciences. The design experience is incorporated across a variety of subject areas and increases in amount and complexity. In addition, the MFE Program is addressing the desired outcomes defined by the Society for Manufacturing Engineers (SME). It had put in place the mechanisms to ensure that by the time of graduation, the graduating seniors do possess:
- Proficiency in materials and manufacturing processes: understanding the behavior and properties of materials as they are altered and influenced by processing in manufacturing.
- Proficiency in process, assembly, and product engineering: understanding the design of products and the equipment, tooling and environment necessary for their manufacture.
- Proficiency in manufacturing competitiveness: understanding the creation of competitive advantage through manufacturing planning, strategy, and control.
- Proficiency in manufacturing systems design: understanding the analysis, synthesis and control of manufacturing operations using statistical and calculus-based methods, simulation, and information technology.
- Proficiency in laboratory practices: graduates must be able to measure manufacturing process variables in a manufacturing laboratory and make technical inferences about the process.
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING — Marauder Lifestyle Courses: USS 1000 and 1 semester credit from Physical Activity (List A); Marauder Foundation Core Courses: ENG 1100 or ENG 1101, MTH 2502, and HIS 1110, HIS 1121 or HIS 1122; Marauder Foundation Bridge Courses: ENG 1102, 3 hours from Humanities (List B); 6 hours in two disciplines from Social and Behavioral Sciences (List C); CHM 1201, CHM 1202, PHY 2411, PHY 2412, MTH 2503, and MTH 3110.
All manufacturing engineering majors must take the following major requirements: INT 1210, MFE 1110, MFE 1210, MFE 2310, MFE 2320, MFE 2410, MFE 2420, MFE 2430, MFE 2440, MFE 3510, MFE 3520, MFE 3530, MFE 3540, MFE 3550, MFE 3610, MFE 3620, MFE 3630, MFE 3640, MFE 4710, MFE 4720, MFE 4730, MFE 4795, MFE 4810, MFE 4820, MFE 4895. A grade of “C” or better in these courses is required to earn a major degree in Manufacturing Engineering.
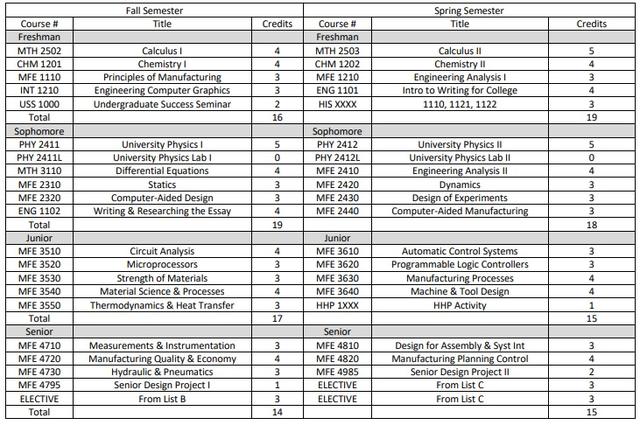
SUGGESTED CURRICULUM FOR THE DEGREE, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE MAJOR IN MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING The curriculum below is to be used in consultation with an academic advisor. The student must be familiar with the University requirements, the General Education Requirements, and any Special Requirements for the above degree.
Minimum hours needed to obtain a Bachelor of Science in Manufacturing Engineering – 123
